Let's Talk Food: 5 Of The Most Common Dietary Restrictions All Events Planners Must Be Aware Of

Some main reasons people rely on particular diets or adhere to dietary restrictions include food allergies or sensitivities, religious beliefs, and ideological convictions.
Some limits are set to protect people’s lives, while others align with your guest’s moral and philosophical principles. They are equally crucial in either case.
Therefore, as an event planner or caterer, educating yourself on some of the most frequent dietary restrictions would be helpful. Here are five dietary restrictions that you need to be aware of.
Lactose Intolerance
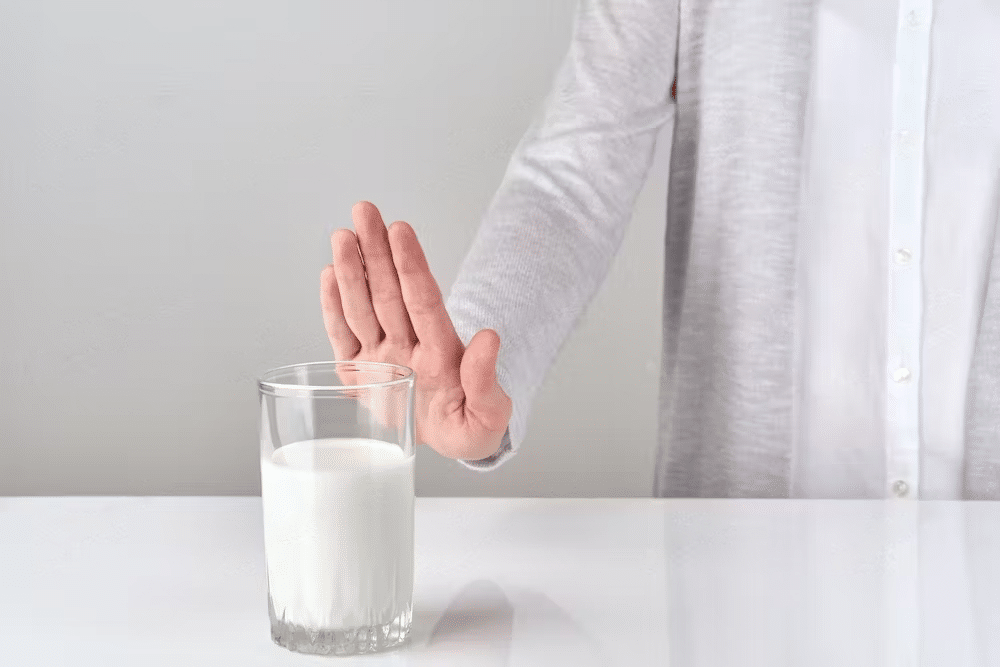

Lactose intolerance is a common dietary requirement for individuals who cannot digest lactose, a type of sugar found in milk and dairy products. Lactose intolerance occurs when the body does not produce enough of the enzyme lactase, which is responsible for breaking down lactose in the digestive system.
Some common dietary requirements for individuals with lactose intolerance include:
- Avoiding milk and dairy products: This includes cow’s milk, cheese, yoghurt, ice cream, and other dairy-based products.
- Choosing lactose-free alternatives: Many dairy products, such as milk and cheese, are available in lactose-free versions that can be a good alternative for individuals with lactose intolerance.
- Eating plant-based foods: Plant-based foods, such as fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes, are naturally lactose-free and can be a good source of nutrients for individuals with lactose intolerance.
Gluten Intolerance Or Sensitivity
Gluten intolerance, also known as celiac disease or non-celiac gluten sensitivity, is a common dietary requirement for individuals who cannot tolerate gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. Gluten intolerance occurs when the body’s immune system reacts to gluten, causing damage to the small intestine and interfering with the absorption of nutrients.
Some common dietary requirements for individuals with gluten intolerance include:
- Avoid foods that contain gluten: This includes bread, pasta, cereal, baked goods, and many processed foods. Individuals with gluten intolerance must be diligent about reading food labels and identifying hidden sources of gluten in food.
- Choosing gluten-free alternatives: Many foods that contain gluten, such as bread and pasta, are available in gluten-free versions that are made with alternative flour, such as rice, corn, or quinoa.
- Eating naturally gluten-free foods: Fruits, vegetables, meats, fish, and most dairy products are naturally gluten-free and can be a good source of nutrients for individuals with gluten intolerance.
Vegetarianism
Vegetarianism is a dietary requirement for individuals who choose to abstain from eating meat, poultry, and fish for various reasons, including ethical, environmental, and health considerations.
Some common dietary requirements for individuals following a vegetarian diet include:
- Getting enough protein: Protein is an essential nutrient found in meat, poultry, fish, and dairy products. Vegetarians can get enough protein by incorporating plant-based sources such as legumes, nuts, seeds, and soy products into their diet.
- Getting enough iron: Iron is important for producing haemoglobin, which carries oxygen throughout the body. Vegetarians can get enough iron by eating iron-rich plant-based foods such as dark leafy greens, beans, and fortified grains.
- Getting enough vitamin B12: The B12 vitamin is primarily found in animal products and is essential for producing red blood cells and maintaining normal nervous system function. Vegetarians can get enough vitamin B12 by eating fortified foods or taking supplements.
- Getting enough calcium and vitamin D: Calcium and vitamin D are important for bone health. Vegetarians can get enough calcium from plant-based sources such as fortified soy milk, tofu, and dark leafy greens. They can also get enough vitamin D from sunlight exposure or fortified foods.
Veganism
Veganism excludes all animal products, including meat, poultry, fish, dairy products, eggs, honey, and any products that contain these ingredients. Individuals who follow a vegan diet do so for various reasons, including ethical, environmental, and health considerations.
Some common dietary requirements for individuals following a vegan diet include:
- Getting enough protein: Protein is an essential nutrient found in meat, poultry, fish, and dairy products. Vegans can get enough protein by incorporating plant-based sources such as legumes, nuts, seeds, and soy products into their diet.
- Getting enough iron: Iron is important for producing haemoglobin, which carries oxygen throughout the body. Vegans can get enough iron by eating iron-rich plant-based foods such as dark leafy greens, beans, and fortified grains.
- Getting enough vitamin B12: Vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal products and is essential to producing red blood cells. Vegans can get enough vitamin B12 by eating fortified foods or taking supplements.
- Getting enough calcium and vitamin D: Calcium and vitamin D are important for bone health. Vegans can get enough calcium from plant-based sources such as fortified soy milk, tofu, and dark leafy greens and can get enough vitamin D from sunlight exposure or fortified foods.
- Getting enough omega-3 fatty acids: Omega-3 fatty acids are important for brain and heart health. Vegans can get enough omega-3 fatty acids by eating flaxseeds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, and walnuts.
Kosher
Kosher is a dietary requirement that is based on Jewish dietary laws. The main principles of kosher dietary laws include the following:
- The prohibition of certain animals.
- The separation of meat and dairy products.
- The use of specific preparation methods.
Some common dietary requirements for individuals following a kosher diet include:
- Avoiding certain animals: The Torah prohibits the consumption of certain animals, including pigs, shellfish, and some types of insects. Meat from permitted animals must be prepared in a specific way to be considered kosher.
- Separation of meat and dairy products: Meat and dairy products cannot be consumed or cooked together and must be stored separately.
- Using specific preparation methods: Meat must be slaughtered in a specific way, and any blood must be drained before consumption. Additionally, certain animal parts, such as the sciatic nerve and certain fats, are prohibited.
- Use of kosher-certified products: Many processed foods, such as baked goods and snacks, must be certified as kosher by a rabbi or a kosher certification agency.
Conclusion
Eating is a fundamental part of life, making it essential to understand common dietary requirements to ensure the health, inclusivity, and safety of those consuming meals. Regarding food-related social situations and the food industry, understanding dietary restrictions is essential for providing a safe and enjoyable eating experience for all involved.
If you’re catering an event, ask your clients if they have any concerns. With that in mind, you will deliver bespoke services that will keep your clients coming for more.
FAQs
Why do people have dietary requirements?
A special diet cannot be selected freely from the main choices available. This could be due to an allergy, intolerance or other medical need; or because children are following a religious or cultural diet; or a vegetarian or vegan diet.
How do you ask if your clients have dietary requirements?
Ensure you include a line about dietary requirements on your wedding invitation or the RSVP card. Writing something like, “Please let us know if you have any dietary requirements” is perfect.
What methods do you use to assess dietary needs?
The most common methods used in nutrition research are the diet record, 24HR, and FFQ. Each method has benefits and drawbacks; however, the 24HR is the most accurate means to assess food and nutrient intake.
References and Citations:
https://www.britannica.com/topic/vegetarianism
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Veganism